COMMERCIAL SEPTIC INSTALLATION IN PARKER COUNTY
Get A Septic System For yoUr Business
Looking for a new commercial septic system? We can match you with the perfect system for your business needs and install it all for you.
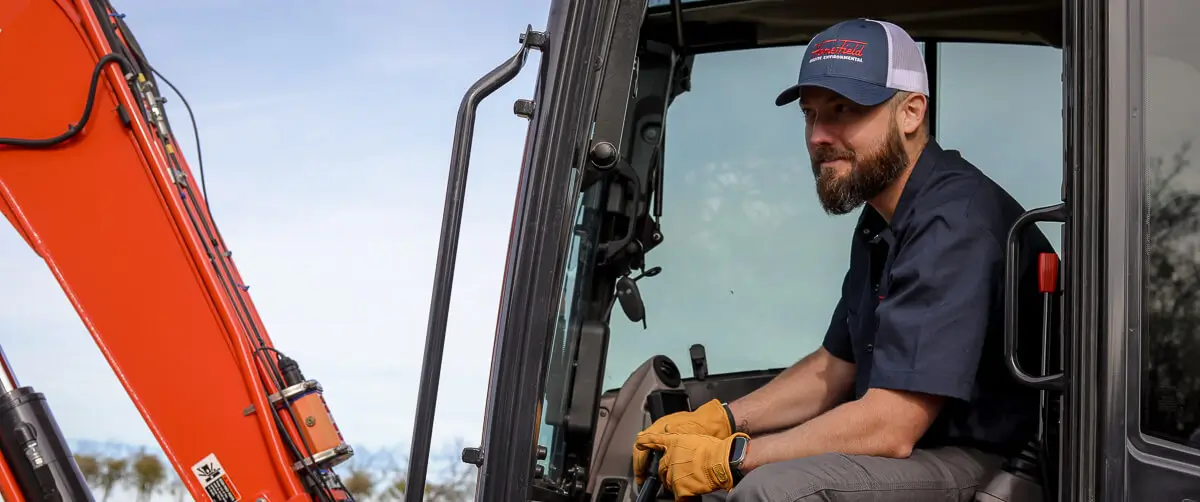

We’ll make sure your next commercial septic system installation meets the needs of your business while also meeting all Parker County regulations.

What To Consider With
A Septic Install
Whether you’re starting a new venture or have outgrown your old septic system, our commercial septic installations get you the right system for your business needs.
Top Questions To Consider:
- Are You Needing A Completely New System?
- Did Something Damage Your Old System?
- Or Did You Outgrow Your Old Septic System?
- Is Your Septic System Up To Code?
- Does Your Current System Allow For Growth?
Put Your Shovel Down And Let Us Install Your Commercial Septic System
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT
Commercial Septic Installation
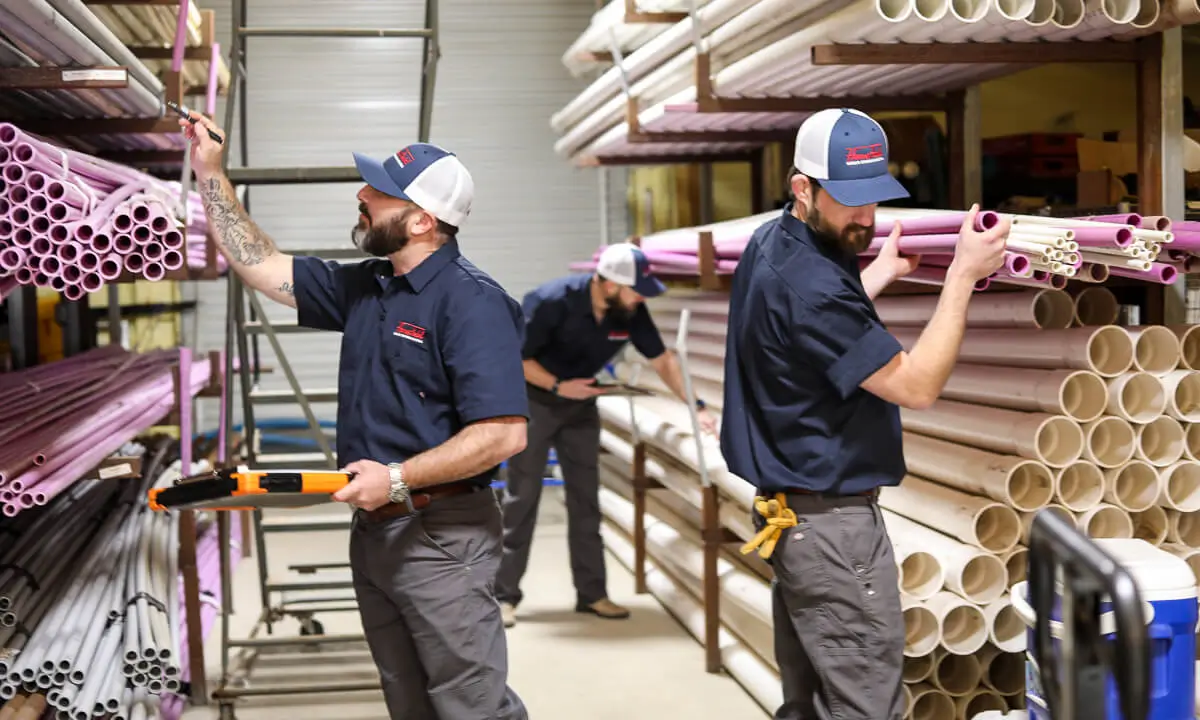

What Is The Best Septic System For Your Local Business?
You need to answer a specific set of questions to choose the best septic system for your local business. Who will use your system, what type of business you are running, and where your property is located are all good starters. Then we need to think through soil conditions and your future growth projections.
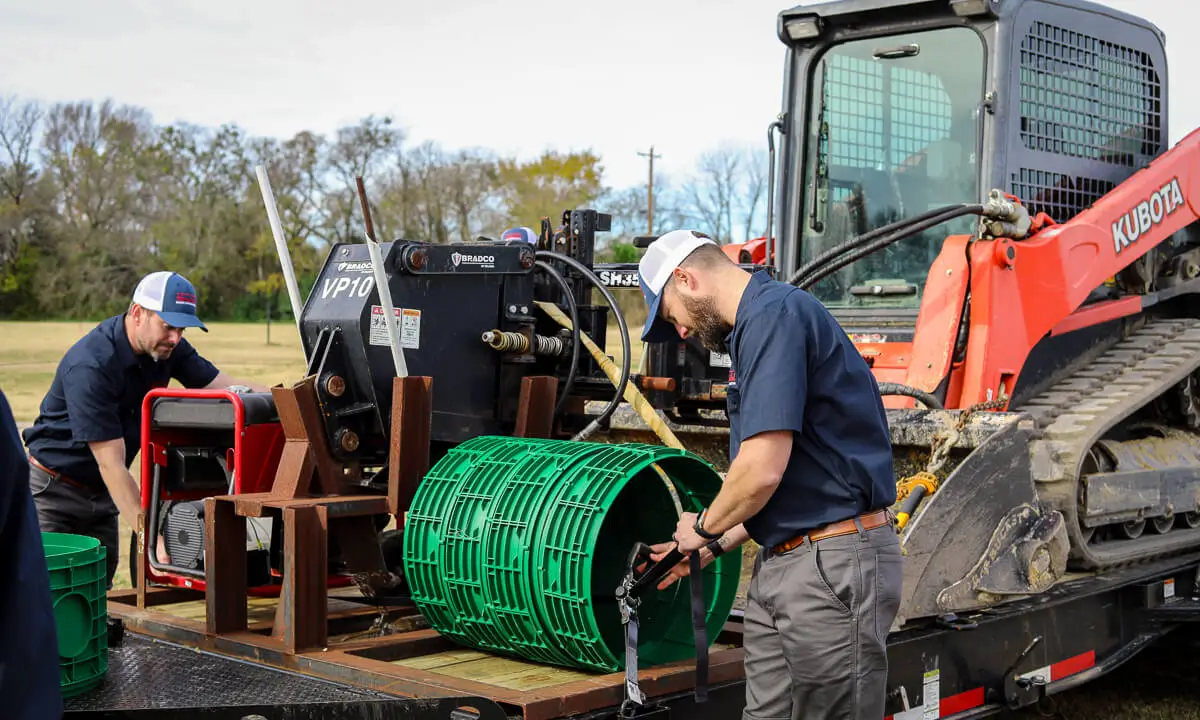

What Should A Commercial Septic Installation Cost?
Similar to what type of system is best for you, the cost of your commercial septic installation is contingent on the scope and size of the project. The needs of your business, the size of your property, and how easy it is to access your property are all factors that can grow or shrink the cost of your commercial septic installation.
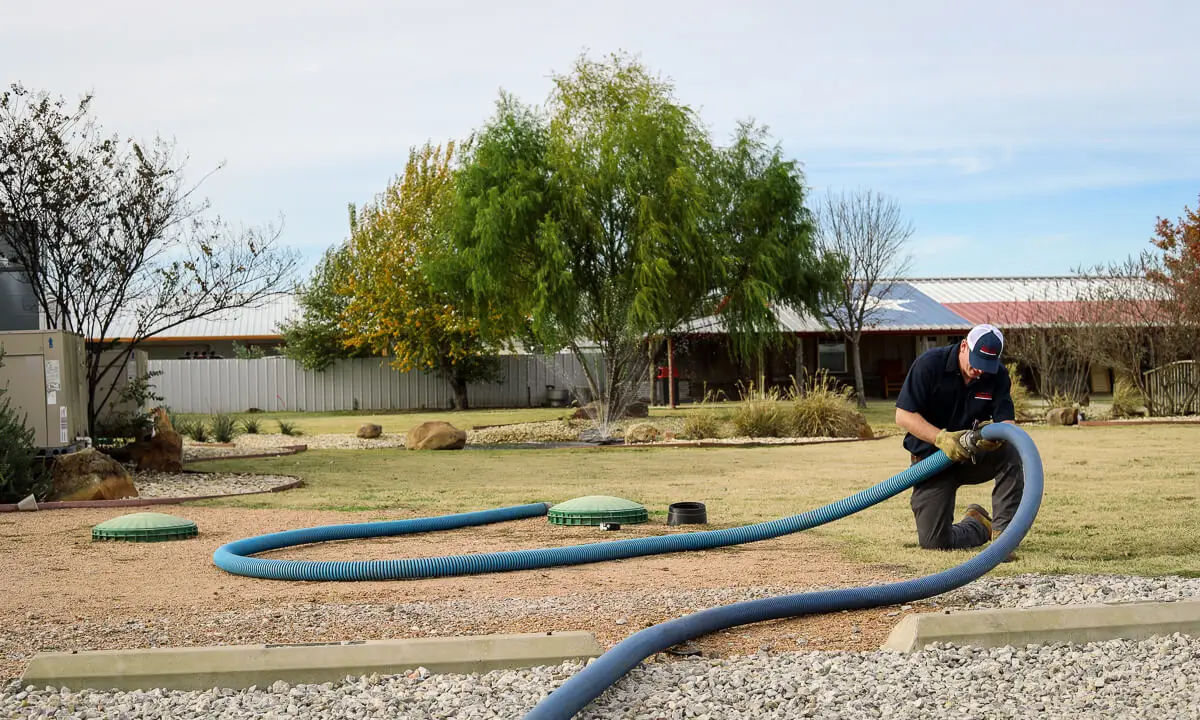

What Do I Need To Do As A Business Septic System Owner?
As a commercial septic system owner, you have a responsibility to understand your system, observe it to make sure it’s working properly (or get help if you’re not sure it is), and follow all the safety rules and requirements for your system.
- Don’t use vehicles on or near your system. You’d think that would be obvious, but a common way septic tanks and disposal fields get damaged is when an owner forgets and drives over a part of it.
- Your septic system will never produce water that’s safe for human or animal consumption. Your system produces water safe for the environment to process, but keep any pets, customers, and employees away from your system and its components, just in case.
- To keep your system healthy, avoid putting non-biodegradable materials (like plastics, coffee grounds, etc), chemicals, grease, oil, solvents, paints, or things like that into your system.
Finally, if your system is an aerobic one, you need to make sure your aerator is clear of water, fire ants (how we hate them here in Texas), or rodents.

How Long Does It Take To Install A New Septic System?
It really depends. Residential systems can be installed as quickly as a few weeks, depending on permitting, but there are many more factors to consider with a commercial installation. The type of system you want to install (aerobic or conventional), the size and complexity of your system
Managing a septic system in unincorporated areas of Parker County, Texas, requires adherence to specific regulations to ensure environmental safety and system efficiency. Here are the key considerations: 1. Permitting Requirements: 2. Local Regulations in Parker County: The Parker County Permitting Department oversees OSSFs in unincorporated areas. They regulate and issue permits for septic systems to ensure compliance with health and safety standards. 3. System Design and Maintenance: 4. Emergency Repairs: While emergency repairs (e.g., replacing tank lids, inlet and outlet devices) do not require a permit, they must be reported to the permitting authority in writing within 72 hours after repairs have begun. 5. Compliance and Inspections: For detailed information and assistance, contact the Parker County Permitting Department: Ensuring compliance with these regulations will help maintain the functionality of your septic system and protect the local environment. You can read more about compliance at this link: TCEQ Maintaining an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, in unincorporated areas of Parker County, Texas, requires adherence to specific operational and maintenance protocols to ensure environmental safety and system efficiency. Below are the key requirements and recommendations: 1. Routine Maintenance: 2. Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs): Maintenance Contracts: ATUs, which provide advanced treatment of wastewater, require more frequent maintenance. Texas regulations mandate that these systems be covered by a continuous service policy for the first two years after installation. After this period, homeowners must either renew the maintenance contract or, if qualified, maintain the system themselves. Self-Maintenance Eligibility: To personally maintain an ATU, homeowners must complete a Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ)-approved course on aerobic system maintenance. This ensures they have the necessary knowledge to manage the system effectively. 3. Reporting and Inspections: Routine Inspections: For systems under a maintenance contract, the service provider is required to perform inspections and submit reports to the local permitting authority. The frequency of these inspections is typically every four months, resulting in three reports per year. Self-Maintained Systems: Homeowners who have opted to maintain their own systems must adhere to the same inspection schedule and are responsible for submitting reports to the Parker County Permitting Department within 14 days of each inspection. 4. Regulatory Compliance: Permitting: Any construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF requires a permit from the Parker County Permitting Department. Unauthorized work can lead to penalties and potential system failures. Licensed Professionals: All maintenance and repair work should be conducted by professionals licensed by the TCEQ, ensuring that all tasks meet state and local standards. 5. Additional Recommendations: Water Conservation: Implementing water-saving measures reduces the load on your septic system, prolonging its lifespan and efficiency. Proper Waste Disposal: Avoid disposing of non-biodegradable items, grease, or hazardous chemicals down the drain, as they can disrupt the system's operation and lead to contamination. Regular Inspections: Even with routine maintenance, periodic professional inspections can help identify potential issues before they become major problems. By adhering to these guidelines and maintaining open communication with the Parker County Permitting Department, you can ensure the longevity and proper functioning of your septic system, safeguarding both your property and the environment. An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. To install or modify an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) in unincorporated areas of Parker County, Texas, you must adhere to specific application requirements set forth by the Parker County Permitting Department and the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Application Submission: 2. Supporting Materials: 3. Fees: 4. Review and Approval Process: 5. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with the Parker County Permitting Department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field In Parker County, Texas, maintaining compliance for your on-site sewage facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, involves adhering to specific renewal and reporting requirements. These requirements can vary based on the type of system you have and your specific location within the county. 1. Maintenance Contracts: Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs): These systems typically require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. The Texas Health and Safety Code mandates that aerobic systems be covered by a continuous service policy for the first two years after installation. After this initial period, homeowners must either renew the maintenance contract or, if qualified, maintain the system themselves. Self-maintenance is permissible only if the homeowner has completed a TCEQ-approved course on aerobic system maintenance. Renewal Frequency: Maintenance contracts are typically renewed annually. It's essential to ensure that your system is always under a valid contract to comply with state and local regulations. 2. Reporting Requirements: Routine Inspections: For systems under a maintenance contract, the service provider is required to perform inspections and submit reports to the local permitting authority. The frequency of these inspections and reports is generally every four months, resulting in three reports per year. However, if your system is equipped with advanced electronic monitoring, the reporting frequency may be reduced to every six months. Self-Maintained Systems: If you're maintaining the system yourself, you must adhere to the same inspection and reporting schedule. Reports should detail the system's operational status, any maintenance performed, and any issues identified. These reports must be submitted to the Parker County Permitting Department within 14 days of the inspection. 3. Local Ordinances: Recommendations: Stay Informed: Regularly consult with the Parker County Permitting Department and your local city authorities to stay updated on any changes in regulations or requirements. Maintain Records: Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities, contracts, and reports. This documentation is crucial for compliance and can be beneficial if any issues arise. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any service providers you hire are licensed and familiar with both state and local regulations pertaining to septic systems. By adhering to these guidelines and maintaining open communication with local authorities, you can ensure your septic system remains compliant and functions efficiently. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ Managing an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires adherence to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate OSSFs within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Parker mandates that septic system plans, drawings, and final inspection reports be filed with the city prior to the house's final approval. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than maintaining a private septic system. The City of Parker, for instance, requires connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. In Parker County, Texas, the Parker County Permitting Department serves as the Authorized Agent for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) concerning On-Site Sewage Facilities (OSSFs), commonly known as septic systems. As the Authorized Agent, the department is responsible for implementing and enforcing state regulations related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs within the county. Key Responsibilities of the Parker County Permitting Department as an Authorized Agent: Permitting and Plan Review: Inspections: Enforcement and Compliance: Public Education and Assistance: By fulfilling these responsibilities, the Parker County Permitting Department ensures that on-site sewage systems are designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that safeguards public health and preserves environmental quality. Contact Information: For detailed information on application procedures, required documentation, and other OSSF-related inquiries, it is advisable to contact the department directly or visit their official website. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. Managing a septic system within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires compliance with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here are the key considerations: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Reno has established ordinances governing the installation and maintenance of septic systems to prevent health hazards and environmental pollution. These ordinances may include requirements such as obtaining permits for all OSSF-related work, regardless of property size, and mandating that maintenance be performed by licensed professionals or homeowners who have completed approved maintenance courses. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than installing or maintaining a private septic system. For instance, the City of Parker mandates connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ In unincorporated areas of Parker County, Texas, the installation, modification, or repair of an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, requires adherence to specific approval and inspection procedures. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Application and Approval Process: Permit Requirement: Before commencing any construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF, you must obtain a permit from the Parker County Permitting Department. Unauthorized construction can lead to civil and administrative penalties. Application Submission: Complete the "On-Site Sewage Facility Application," providing detailed information about your property and the proposed system. This includes a site evaluation conducted by a licensed Site Evaluator or Professional Engineer to assess soil suitability and site-specific conditions. System Design: Based on the site evaluation, develop a system design that complies with state and local regulations. The design should include detailed plans and specifications of the proposed OSSF. 2. Inspection Process: Construction Inspection: After obtaining the permit and during the installation of the OSSF, but before covering any components, you must schedule an inspection with the Parker County Permitting Department. This inspection ensures the system is installed according to the approved plans and complies with regulatory standards. Final Approval: Once the system passes the inspection, you'll receive authorization to operate the OSSF. It's crucial to ensure that all components are accessible and that the system is functioning correctly before the final approval. 3. Additional Considerations: Maintenance Requirements: Certain systems, especially aerobic treatment units, may require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. Ensure you understand and comply with any ongoing maintenance requirements to keep the system functioning properly and in compliance with regulations. Regulatory Compliance: Always verify with the Parker County Permitting Department for any updates or changes to application requirements or regulations before proceeding. Staying informed ensures compliance and helps avoid potential issues. Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and maintaining open communication with the Parker County Permitting Department, you can ensure a smooth approval and inspection process for your septic system in unincorporated areas of Parker County. You can find the Parker County Permitting Application here: https://www.parkercountytx.gov/DocumentCenter/View/10724/Parker-County-Septic-Application-and-Tech-Sheet The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field Managing an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires adherence to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate OSSFs within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Parker mandates that septic system plans, drawings, and final inspection reports be filed with the city prior to the house's final approval. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than maintaining a private septic system. The City of Parker, for instance, requires connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Willow Park, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Application Submission: Obtain Application Forms: The City of Willow Park requires that all OSSFs be permitted as part of the building permit process for new construction, repairs, or remodeling projects. You can access the necessary application forms through the city's official website. Site Evaluation: A licensed Site Evaluator or Professional Engineer must conduct a site and soil evaluation to determine the suitability of your property for an OSSF. This evaluation is crucial for designing an effective system. System Design: Based on the site evaluation, develop a system design that complies with state and local regulations. The design should include detailed plans and specifications of the proposed OSSF. 2. Supporting Materials: Property Plat or Survey: Provide a detailed plat or survey of your property, clearly indicating boundaries, existing structures, proposed OSSF location, and distances from property lines and water sources. Soil Analysis Report: Include the results of the soil analysis conducted during the site evaluation, highlighting soil types and their suitability for wastewater absorption. Floodplain Information: If applicable, provide documentation indicating whether the proposed OSSF location is within a floodplain. Compliance with floodplain regulations is mandatory. 3. Fees: 4. Review and Approval Process: Plan Review: Upon submission, the Planning & Development Department will review your application and supporting materials to ensure compliance with all regulations. Inspections: After installation, but before covering any components, schedule an inspection with the department to verify that the system is installed according to the approved plans and standards. Approval: Once the system passes inspection, you'll receive authorization to operate the OSSF. 5. Additional Considerations: Connection to Public Sewer: The City of Willow Park mandates that no permit shall be issued for an OSSF if a public sanitary sewer is available. Ensure that your property does not have access to a public sewer system before applying for an OSSF permit. Maintenance Contracts: Certain systems, especially aerobic treatment units, may require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. Ensure you understand and comply with any ongoing maintenance requirements. Regulatory Compliance: Always verify with the Planning & Development Department for any updates or changes to application requirements or regulations before proceeding. Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with the City's Planning & Development Department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. When planning to install or modify an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Willow Park, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Application Submission: Obtain Application Forms: The City of Willow Park requires that all OSSFs be permitted prior to installation or modification. You can access the necessary application forms through the city's official website under the Planning & Development Department's Permit Applications section. Site Evaluation: A licensed Site Evaluator or Professional Engineer must conduct a site and soil evaluation to determine the suitability of your property for an OSSF. This evaluation is crucial for designing an effective system. System Design: Based on the site evaluation, develop a system design that complies with state and local regulations. The design should include detailed plans and specifications of the proposed OSSF. 2. Supporting Materials: Property Plat or Survey: Provide a detailed plat or survey of your property, clearly indicating boundaries, existing structures, proposed OSSF location, and distances from property lines and water sources. Soil Analysis Report: Include the results of the soil analysis conducted during the site evaluation, highlighting soil types and their suitability for wastewater absorption. Floodplain Information: If applicable, provide documentation indicating whether the proposed OSSF location is within a floodplain. Compliance with floodplain regulations is mandatory. 3. Fees: 4. Review and Approval Process: Plan Review: Upon submission, the Planning & Development Department will review your application and supporting materials to ensure compliance with all regulations. Inspections: After installation, but before covering any components, schedule an inspection with the department to verify that the system is installed according to the approved plans and standards. Approval: Once the system passes inspection, you'll receive authorization to operate the OSSF. 5. Additional Considerations: Connection to Public Sewer: The City of Willow Park mandates that no permit shall be issued for an OSSF if a public sanitary sewer is available. Ensure that your property does not have access to a public sewer system before applying for an OSSF permit. Maintenance Contracts: Certain systems, especially aerobic treatment units, may require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. Ensure you understand and comply with any ongoing maintenance requirements. Regulatory Compliance: Always verify with the Planning & Development Department for any updates or changes to application requirements or regulations before proceeding. Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with the City's Planning & Development Department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. Managing a septic system within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires compliance with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here are the key considerations: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Reno has established ordinances governing the installation and maintenance of septic systems to prevent health hazards and environmental pollution. These ordinances may include requirements such as obtaining permits for all OSSF-related work, regardless of property size, and mandating that maintenance be performed by licensed professionals or homeowners who have completed approved maintenance courses. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than installing or maintaining a private septic system. For instance, the City of Parker mandates connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field In Parker County, Texas, maintaining compliance for your on-site sewage facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, involves adhering to specific renewal and reporting requirements. These requirements can vary based on the type of system you have and your specific location within the county. 1. Maintenance Contracts: Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs): These systems typically require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. The Texas Health and Safety Code mandates that aerobic systems be covered by a continuous service policy for the first two years after installation. After this initial period, homeowners must either renew the maintenance contract or, if qualified, maintain the system themselves. Self-maintenance is permissible only if the homeowner has completed a TCEQ-approved course on aerobic system maintenance. Renewal Frequency: Maintenance contracts are typically renewed annually. It's essential to ensure that your system is always under a valid contract to comply with state and local regulations. 2. Reporting Requirements: Routine Inspections: For systems under a maintenance contract, the service provider is required to perform inspections and submit reports to the local permitting authority. The frequency of these inspections and reports is generally every four months, resulting in three reports per year. However, if your system is equipped with advanced electronic monitoring, the reporting frequency may be reduced to every six months. Self-Maintained Systems: If you're maintaining the system yourself, you must adhere to the same inspection and reporting schedule. Reports should detail the system's operational status, any maintenance performed, and any issues identified. These reports must be submitted to the Parker County Permitting Department within 14 days of the inspection. 3. Local Ordinances: Recommendations: Stay Informed: Regularly consult with the Parker County Permitting Department and your local city authorities to stay updated on any changes in regulations or requirements. Maintain Records: Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities, contracts, and reports. This documentation is crucial for compliance and can be beneficial if any issues arise. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any service providers you hire are licensed and familiar with both state and local regulations pertaining to septic systems. By adhering to these guidelines and maintaining open communication with local authorities, you can ensure your septic system remains compliant and functions efficiently. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ Managing an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires adherence to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate OSSFs within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Parker mandates that septic system plans, drawings, and final inspection reports be filed with the city prior to the house's final approval. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than maintaining a private septic system. The City of Parker, for instance, requires connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. When planning to install or modify an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Hudson Oaks, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Application Submission: Obtain Application Forms: The City of Hudson Oaks requires that all OSSFs be permitted prior to installation or modification. You can access the necessary application forms through the city's official website. Site Evaluation: A licensed Site Evaluator or Professional Engineer must conduct a site and soil evaluation to determine the suitability of your property for an OSSF. This evaluation is crucial for designing an effective system. System Design: Based on the site evaluation, develop a system design that complies with state and local regulations. The design should include detailed plans and specifications of the proposed OSSF. 2. Supporting Materials: Property Plat or Survey: Provide a detailed plat or survey of your property, clearly indicating boundaries, existing structures, proposed OSSF location, and distances from property lines and water sources. Soil Analysis Report: Include the results of the soil analysis conducted during the site evaluation, highlighting soil types and their suitability for wastewater absorption. Floodplain Information: If applicable, provide documentation indicating whether the proposed OSSF location is within a floodplain. Compliance with floodplain regulations is mandatory. 3. Fees: 4. Review and Approval Process: Plan Review: Upon submission, the Permits Department will review your application and supporting materials to ensure compliance with all regulations. Inspections: After installation, but before covering any components, schedule an inspection with the department to verify that the system is installed according to the approved plans and standards. Approval: Once the system passes inspection, you'll receive authorization to operate the OSSF. 5. Additional Considerations: Connection to Public Sewer: The City of Hudson Oaks mandates that no permit shall be issued for an OSSF if a public sanitary sewer is available. Ensure that your property does not have access to a public sewer system before applying for an OSSF permit. Maintenance Contracts: Certain systems, especially aerobic treatment units, may require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. Ensure you understand and comply with any ongoing maintenance requirements. Regulatory Compliance: Always verify with the Permits Department for any updates or changes to application requirements or regulations before proceeding. Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with the City's Permits Department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. In Parker County, Texas, the Parker County Permitting Department serves as the Authorized Agent for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) concerning On-Site Sewage Facilities (OSSFs), commonly known as septic systems. As the Authorized Agent, the department is responsible for implementing and enforcing state regulations related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs within the county. Key Responsibilities of the Parker County Permitting Department as an Authorized Agent: Permitting and Plan Review: Inspections: Enforcement and Compliance: Public Education and Assistance: By fulfilling these responsibilities, the Parker County Permitting Department ensures that on-site sewage systems are designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that safeguards public health and preserves environmental quality. Contact Information: For detailed information on application procedures, required documentation, and other OSSF-related inquiries, it is advisable to contact the department directly or visit their official website. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. Managing a septic system within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires compliance with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here are the key considerations: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Reno has established ordinances governing the installation and maintenance of septic systems to prevent health hazards and environmental pollution. These ordinances may include requirements such as obtaining permits for all OSSF-related work, regardless of property size, and mandating that maintenance be performed by licensed professionals or homeowners who have completed approved maintenance courses. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than installing or maintaining a private septic system. For instance, the City of Parker mandates connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Wise County, Texas, it's essential to comply with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. In Wise County, Texas, the Environmental Services Department serves as the Authorized Agent for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) concerning On-Site Sewage Facilities (OSSFs), commonly known as septic systems. This designation empowers the department to implement and enforce state regulations related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs within the county. Key Responsibilities of the Wise County Environmental Services Department as an Authorized Agent: Permitting and Plan Review: Inspections: Enforcement and Compliance: Public Education and Assistance: By fulfilling these responsibilities, the Wise County Environmental Services Department ensures that on-site sewage systems are designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that safeguards public health and preserves environmental quality. Contact Information: For detailed information on application procedures, required documentation, and other OSSF-related inquiries, it is advisable to contact the department directly or visit their official website. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field When planning to install or modify an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of any municipality in Erath County, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: Obtain Application Forms: Reach out to your city's permitting department to acquire the necessary OSSF permit application forms. These forms typically require detailed information about your property and the proposed septic system. Site Evaluation: A licensed Site Evaluator or Professional Engineer must conduct a site and soil evaluation to determine the suitability of your property for an OSSF. This evaluation is crucial for designing an effective system. System Design: Based on the site evaluation, develop a system design that complies with state and local regulations. The design should include detailed plans and specifications of the proposed OSSF. 3. Supporting Materials: Property Plat or Survey: Provide a detailed plat or survey of your property, clearly indicating boundaries, existing structures, proposed OSSF location, and distances from property lines and water sources. Soil Analysis Report: Include the results of the soil analysis conducted during the site evaluation, highlighting soil types and their suitability for wastewater absorption. Floodplain Information: If applicable, provide documentation indicating whether the proposed OSSF location is within a floodplain. Compliance with floodplain regulations is mandatory. 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: Plan Review: Upon submission, the permitting department will review your application and supporting materials to ensure compliance with all regulations. Inspections: After installation, but before covering any components, schedule an inspection with the permitting department to verify that the system is installed according to the approved plans and standards. Approval: Once the system passes inspection, you'll receive authorization to operate the OSSF. 6. Additional Considerations: Maintenance Contracts: Certain systems, especially aerobic treatment units, may require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. Ensure you understand and comply with any ongoing maintenance requirements. Regulatory Compliance: Always verify with your city's permitting department for any updates or changes to application requirements or regulations before proceeding. Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. In Erath County, Texas, the Environmental Health Department serves as the Authorized Agent for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) concerning On-Site Sewage Facilities (OSSFs), commonly known as septic systems. This designation empowers the department to implement and enforce state regulations related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs within the county. Key Responsibilities of the Erath County Environmental Health Department as an Authorized Agent: Permitting and Plan Review: Inspections: Enforcement and Compliance: Public Education and Assistance: By fulfilling these responsibilities, the Erath County Environmental Health Department ensures that on-site sewage systems are designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that safeguards public health and preserves environmental quality. Contact Information: For detailed information on application procedures, required documentation, and other OSSF-related inquiries, it is advisable to contact the department directly or visit their official website. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field When planning to install or modify an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of any municipality in Palo Pinto County, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. In Palo Pinto County, Texas, the Public Works Department serves as the Authorized Agent for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) concerning On-Site Sewage Facilities (OSSFs), commonly known as septic systems. This designation empowers the department to implement and enforce state regulations related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs within the county. Key Responsibilities of the Palo Pinto County Public Works Department as an Authorized Agent: Permitting and Plan Review: Inspections: Enforcement and Compliance: Public Education and Assistance: By fulfilling these responsibilities, the Palo Pinto County Public Works Department ensures that on-site sewage systems are designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that safeguards public health and preserves environmental quality. Contact Information: For detailed information on application procedures, required documentation, and other OSSF-related inquiries, it is advisable to contact the department directly or visit their official website. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Hood County, Texas, it's essential to comply with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. When planning to install or modify an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Granbury, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Application Submission: Obtain Application Forms: The City of Granbury requires that all OSSFs be permitted prior to installation or modification. You can access the necessary application forms through the city's official website or by visiting the Building Inspections, Permits & Code Enforcement Department located on the first floor of Granbury City Hall, 116 W Bridge St, Granbury, TX 76048. Site Evaluation: A licensed Site Evaluator or Professional Engineer must conduct a site and soil evaluation to determine the suitability of your property for an OSSF. This evaluation is crucial for designing an effective system. System Design: Based on the site evaluation, develop a system design that complies with state and local regulations. The design should include detailed plans and specifications of the proposed OSSF. 2. Supporting Materials: Property Plat or Survey: Provide a detailed plat or survey of your property, clearly indicating boundaries, existing structures, proposed OSSF location, and distances from property lines and water sources. Soil Analysis Report: Include the results of the soil analysis conducted during the site evaluation, highlighting soil types and their suitability for wastewater absorption. Floodplain Information: If applicable, provide documentation indicating whether the proposed OSSF location is within a floodplain. Compliance with floodplain regulations is mandatory. 3. Fees: 4. Review and Approval Process: Plan Review: Upon submission, the Building Inspections, Permits & Code Enforcement Department will review your application and supporting materials to ensure compliance with all regulations. Inspections: After installation, but before covering any components, schedule an inspection with the department to verify that the system is installed according to the approved plans and standards. Approval: Once the system passes inspection, you'll receive authorization to operate the OSSF. 5. Additional Considerations: Maintenance Contracts: Certain systems, especially those requiring ongoing maintenance, may necessitate a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. Ensure you understand and comply with any ongoing maintenance requirements. Regulatory Compliance: Always verify with the Building Inspections, Permits & Code Enforcement Department for any updates or changes to application requirements or regulations before proceeding. Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with the City's Building Inspections, Permits & Code Enforcement Department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. In Hood County, Texas, the Environmental Health Department serves as the Authorized Agent for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) concerning On-Site Sewage Facilities (OSSFs), commonly known as septic systems. This designation empowers the department to implement and enforce state regulations related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs within the county. Key Responsibilities of the Hood County Environmental Health Department as an Authorized Agent: Permitting and Plan Review: Inspections: Enforcement and Compliance: Public Education and Assistance: By fulfilling these responsibilities, the Hood County Environmental Health Department ensures that on-site sewage systems are designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that safeguards public health and preserves environmental quality. Contact Information: For detailed information on application procedures, required documentation, and other OSSF-related inquiries, it is advisable to contact the department directly or visit their official website. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. Managing a septic system within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires compliance with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here are the key considerations: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Reno has established ordinances governing the installation and maintenance of septic systems to prevent health hazards and environmental pollution. These ordinances may include requirements such as obtaining permits for all OSSF-related work, regardless of property size, and mandating that maintenance be performed by licensed professionals or homeowners who have completed approved maintenance courses. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than installing or maintaining a private septic system. For instance, the City of Parker mandates connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Hood County, Texas, it's essential to comply with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. In Hood County, Texas, the Environmental Health Department serves as the Authorized Agent for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) concerning On-Site Sewage Facilities (OSSFs), commonly known as septic systems. This designation empowers the department to implement and enforce state regulations related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs within the county. Key Responsibilities of the Hood County Environmental Health Department as an Authorized Agent: Permitting and Plan Review: Inspections: Enforcement and Compliance: Public Education and Assistance: By fulfilling these responsibilities, the Hood County Environmental Health Department ensures that on-site sewage systems are designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that safeguards public health and preserves environmental quality. Contact Information: For detailed information on application procedures, required documentation, and other OSSF-related inquiries, it is advisable to contact the department directly or visit their official website. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Johnson County, Texas, it's essential to comply with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. When planning to install or modify an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Joshua, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Application Submission: Obtain Application Forms: The City of Joshua requires that all OSSFs be permitted prior to installation or modification. You can access the necessary application forms through the city's official website under the Development Services section. Site Evaluation: A licensed Site Evaluator or Professional Engineer must conduct a site and soil evaluation to determine the suitability of your property for an OSSF. This evaluation is crucial for designing an effective system. System Design: Based on the site evaluation, develop a system design that complies with state and local regulations. The design should include detailed plans and specifications of the proposed OSSF. 2. Supporting Materials: Property Plat or Survey: Provide a detailed plat or survey of your property, clearly indicating boundaries, existing structures, proposed OSSF location, and distances from property lines and water sources. Soil Analysis Report: Include the results of the soil analysis conducted during the site evaluation, highlighting soil types and their suitability for wastewater absorption. Floodplain Information: If applicable, provide documentation indicating whether the proposed OSSF location is within a floodplain. Compliance with floodplain regulations is mandatory. 3. Fees: 4. Review and Approval Process: Plan Review: Upon submission, the Development Services Department will review your application and supporting materials to ensure compliance with all regulations. Inspections: After installation, but before covering any components, schedule an inspection with the department to verify that the system is installed according to the approved plans and standards. Approval: Once the system passes inspection, you'll receive authorization to operate the OSSF. 5. Additional Considerations: Connection to Public Sewer: The City of Joshua mandates that no permit shall be issued for an OSSF if a public sanitary sewer is available. Ensure that your property does not have access to a public sewer system before applying for an OSSF permit. Maintenance Contracts: Certain systems, especially aerobic treatment units, may require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. Ensure you understand and comply with any ongoing maintenance requirements. Regulatory Compliance: Always verify with the Development Services Department for any updates or changes to application requirements or regulations before proceeding. Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with the City's Development Services Department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. In Johnson County, Texas, the Public Works Department serves as the Authorized Agent for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) concerning On-Site Sewage Facilities (OSSFs), commonly known as septic systems. In this capacity, the department is responsible for implementing and enforcing state regulations related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs within the county. Key Responsibilities of the Johnson County Public Works Department as an Authorized Agent: Permitting and Plan Review: Inspections: Enforcement and Compliance: Public Education and Assistance: By fulfilling these responsibilities, the Johnson County Public Works Department ensures that on-site sewage systems are designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that safeguards public health and preserves environmental quality. Contact Information: For detailed information on application procedures, required documentation, and other OSSF-related inquiries, it is advisable to contact the department directly or visit their official website. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. Managing a septic system within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires compliance with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here are the key considerations: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Reno has established ordinances governing the installation and maintenance of septic systems to prevent health hazards and environmental pollution. These ordinances may include requirements such as obtaining permits for all OSSF-related work, regardless of property size, and mandating that maintenance be performed by licensed professionals or homeowners who have completed approved maintenance courses. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than installing or maintaining a private septic system. For instance, the City of Parker mandates connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Johnson County, Texas, it's essential to comply with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. In Johnson County, Texas, the Public Works Department serves as the Authorized Agent for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) concerning On-Site Sewage Facilities (OSSFs), commonly known as septic systems. In this capacity, the department is responsible for implementing and enforcing state regulations related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs within the county. Key Responsibilities of the Johnson County Public Works Department as an Authorized Agent: Permitting and Plan Review: Inspections: Enforcement and Compliance: Public Education and Assistance: By fulfilling these responsibilities, the Johnson County Public Works Department ensures that on-site sewage systems are designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that safeguards public health and preserves environmental quality. Contact Information: For detailed information on application procedures, required documentation, and other OSSF-related inquiries, it is advisable to contact the department directly or visit their official website. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. In Johnson County, Texas, the Public Works Department serves as the Authorized Agent for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) concerning On-Site Sewage Facilities (OSSFs), commonly known as septic systems. In this capacity, the department is responsible for implementing and enforcing state regulations related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs within the county. Key Responsibilities of the Johnson County Public Works Department as an Authorized Agent: Permitting and Plan Review: Inspections: Enforcement and Compliance: Public Education and Assistance: By fulfilling these responsibilities, the Johnson County Public Works Department ensures that on-site sewage systems are designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that safeguards public health and preserves environmental quality. Contact Information: For detailed information on application procedures, required documentation, and other OSSF-related inquiries, it is advisable to contact the department directly or visit their official website. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. Managing a septic system within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires compliance with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here are the key considerations: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Reno has established ordinances governing the installation and maintenance of septic systems to prevent health hazards and environmental pollution. These ordinances may include requirements such as obtaining permits for all OSSF-related work, regardless of property size, and mandating that maintenance be performed by licensed professionals or homeowners who have completed approved maintenance courses. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than installing or maintaining a private septic system. For instance, the City of Parker mandates connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field In Parker County, Texas, maintaining compliance for your on-site sewage facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, involves adhering to specific renewal and reporting requirements. These requirements can vary based on the type of system you have and your specific location within the county. 1. Maintenance Contracts: Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs): These systems typically require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. The Texas Health and Safety Code mandates that aerobic systems be covered by a continuous service policy for the first two years after installation. After this initial period, homeowners must either renew the maintenance contract or, if qualified, maintain the system themselves. Self-maintenance is permissible only if the homeowner has completed a TCEQ-approved course on aerobic system maintenance. Renewal Frequency: Maintenance contracts are typically renewed annually. It's essential to ensure that your system is always under a valid contract to comply with state and local regulations. 2. Reporting Requirements: Routine Inspections: For systems under a maintenance contract, the service provider is required to perform inspections and submit reports to the local permitting authority. The frequency of these inspections and reports is generally every four months, resulting in three reports per year. However, if your system is equipped with advanced electronic monitoring, the reporting frequency may be reduced to every six months. Self-Maintained Systems: If you're maintaining the system yourself, you must adhere to the same inspection and reporting schedule. Reports should detail the system's operational status, any maintenance performed, and any issues identified. These reports must be submitted to the Parker County Permitting Department within 14 days of the inspection. 3. Local Ordinances: Recommendations: Stay Informed: Regularly consult with the Parker County Permitting Department and your local city authorities to stay updated on any changes in regulations or requirements. Maintain Records: Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities, contracts, and reports. This documentation is crucial for compliance and can be beneficial if any issues arise. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any service providers you hire are licensed and familiar with both state and local regulations pertaining to septic systems. By adhering to these guidelines and maintaining open communication with local authorities, you can ensure your septic system remains compliant and functions efficiently. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ Managing an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires adherence to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate OSSFs within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Parker mandates that septic system plans, drawings, and final inspection reports be filed with the city prior to the house's final approval. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than maintaining a private septic system. The City of Parker, for instance, requires connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. When planning to install or modify an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Reno, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Application Submission: Obtain Application Forms: The City of Reno requires that all OSSFs be permitted prior to installation or modification. Permit applications are available at City Hall. Site Evaluation: A licensed Site Evaluator or Professional Engineer must conduct a site and soil evaluation to determine the suitability of your property for an OSSF. This evaluation is crucial for designing an effective system. System Design: Based on the site evaluation, develop a system design that complies with state and local regulations. The design should include detailed plans and specifications of the proposed OSSF. 2. Supporting Materials: Property Plat or Survey: Provide a detailed plat or survey of your property, clearly indicating boundaries, existing structures, proposed OSSF location, and distances from property lines and water sources. Soil Analysis Report: Include the results of the soil analysis conducted during the site evaluation, highlighting soil types and their suitability for wastewater absorption. Floodplain Information: If applicable, provide documentation indicating whether the proposed OSSF location is within a floodplain. Compliance with floodplain regulations is mandatory. 3. Fees: 4. Review and Approval Process: Plan Review: Upon submission, the Building Services Department will review your application and supporting materials to ensure compliance with all regulations. Inspections: After installation, but before covering any components, schedule an inspection with the department to verify that the system is installed according to the approved plans and standards. Approval: Once the system passes inspection, you'll receive authorization to operate the OSSF. 5. Additional Considerations: Licensed Contractors: All OSSF work must be completed by contractors licensed by the State of Texas and registered with the City of Reno. Regulatory Compliance: Always verify with the Building Services Department for any updates or changes to application requirements or regulations before proceeding. Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with the City's Building Services Department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. In Parker County, Texas, the Parker County Permitting Department serves as the Authorized Agent for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) concerning On-Site Sewage Facilities (OSSFs), commonly known as septic systems. As the Authorized Agent, the department is responsible for implementing and enforcing state regulations related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs within the county. Key Responsibilities of the Parker County Permitting Department as an Authorized Agent: Permitting and Plan Review: Inspections: Enforcement and Compliance: Public Education and Assistance: By fulfilling these responsibilities, the Parker County Permitting Department ensures that on-site sewage systems are designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that safeguards public health and preserves environmental quality. Contact Information: For detailed information on application procedures, required documentation, and other OSSF-related inquiries, it is advisable to contact the department directly or visit their official website. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. Managing a septic system within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires compliance with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here are the key considerations: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Reno has established ordinances governing the installation and maintenance of septic systems to prevent health hazards and environmental pollution. These ordinances may include requirements such as obtaining permits for all OSSF-related work, regardless of property size, and mandating that maintenance be performed by licensed professionals or homeowners who have completed approved maintenance courses. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than installing or maintaining a private septic system. For instance, the City of Parker mandates connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Fort Worth, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Application Submission: Obtain Application Forms: The City of Fort Worth requires that all OSSFs be permitted. You can access the necessary application forms through the city's official website. Site Evaluation: A licensed Site Evaluator or Professional Engineer must conduct a site and soil evaluation to determine the suitability of your property for an OSSF. This evaluation is crucial for designing an effective system. System Design: Based on the site evaluation, develop a system design that complies with state and local regulations. The design should include detailed plans and specifications of the proposed OSSF. 2. Supporting Materials: Property Plat or Survey: Provide a detailed plat or survey of your property, clearly indicating boundaries, existing structures, proposed OSSF location, and distances from property lines and water sources. Soil Analysis Report: Include the results of the soil analysis conducted during the site evaluation, highlighting soil types and their suitability for wastewater absorption. Floodplain Information: If applicable, provide documentation indicating whether the proposed OSSF location is within a floodplain. Compliance with floodplain regulations is mandatory. 3. Fees: 4. Review and Approval Process: Plan Review: Upon submission, the Water Department will review your application and supporting materials to ensure compliance with all regulations. Inspections: After installation, but before covering any components, schedule an inspection with the department to verify that the system is installed according to the approved plans and standards. Approval: Once the system passes inspection, you'll receive authorization to operate the OSSF. 5. Additional Considerations: Connection to Public Sewer: The City of Fort Worth mandates that no permit shall be issued for an OSSF if a public sanitary sewer is available. Ensure that your property does not have access to a public sewer system before applying for an OSSF permit. Maintenance Contracts: Certain systems, especially aerobic treatment units, may require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. Ensure you understand and comply with any ongoing maintenance requirements. Regulatory Compliance: Always verify with the Water Department for any updates or changes to application requirements or regulations before proceeding. Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with the City's Water Department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. Managing a septic system within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires compliance with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here are the key considerations: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Reno has established ordinances governing the installation and maintenance of septic systems to prevent health hazards and environmental pollution. These ordinances may include requirements such as obtaining permits for all OSSF-related work, regardless of property size, and mandating that maintenance be performed by licensed professionals or homeowners who have completed approved maintenance courses. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than installing or maintaining a private septic system. For instance, the City of Parker mandates connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field In Parker County, Texas, maintaining compliance for your on-site sewage facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, involves adhering to specific renewal and reporting requirements. These requirements can vary based on the type of system you have and your specific location within the county. 1. Maintenance Contracts: Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs): These systems typically require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. The Texas Health and Safety Code mandates that aerobic systems be covered by a continuous service policy for the first two years after installation. After this initial period, homeowners must either renew the maintenance contract or, if qualified, maintain the system themselves. Self-maintenance is permissible only if the homeowner has completed a TCEQ-approved course on aerobic system maintenance. Renewal Frequency: Maintenance contracts are typically renewed annually. It's essential to ensure that your system is always under a valid contract to comply with state and local regulations. 2. Reporting Requirements: Routine Inspections: For systems under a maintenance contract, the service provider is required to perform inspections and submit reports to the local permitting authority. The frequency of these inspections and reports is generally every four months, resulting in three reports per year. However, if your system is equipped with advanced electronic monitoring, the reporting frequency may be reduced to every six months. Self-Maintained Systems: If you're maintaining the system yourself, you must adhere to the same inspection and reporting schedule. Reports should detail the system's operational status, any maintenance performed, and any issues identified. These reports must be submitted to the Parker County Permitting Department within 14 days of the inspection. 3. Local Ordinances: Recommendations: Stay Informed: Regularly consult with the Parker County Permitting Department and your local city authorities to stay updated on any changes in regulations or requirements. Maintain Records: Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities, contracts, and reports. This documentation is crucial for compliance and can be beneficial if any issues arise. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any service providers you hire are licensed and familiar with both state and local regulations pertaining to septic systems. By adhering to these guidelines and maintaining open communication with local authorities, you can ensure your septic system remains compliant and functions efficiently. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ Managing an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires adherence to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate OSSFs within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Parker mandates that septic system plans, drawings, and final inspection reports be filed with the city prior to the house's final approval. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than maintaining a private septic system. The City of Parker, for instance, requires connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. When planning to install or modify an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Mineral Wells, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Application Submission: Obtain Application Forms: The City of Mineral Wells requires that all OSSFs be permitted prior to installation or repair. You can access the necessary application forms through the city's official website. Site Evaluation: A licensed Site Evaluator or Professional Engineer must conduct a site and soil evaluation to determine the suitability of your property for an OSSF. This evaluation is crucial for designing an effective system. System Design: Based on the site evaluation, develop a system design that complies with state and local regulations. The design should include detailed plans and specifications of the proposed OSSF. 2. Supporting Materials: Property Plat or Survey: Provide a detailed plat or survey of your property, clearly indicating boundaries, existing structures, proposed OSSF location, and distances from property lines and water sources. Soil Analysis Report: Include the results of the soil analysis conducted during the site evaluation, highlighting soil types and their suitability for wastewater absorption. Floodplain Information: If applicable, provide documentation indicating whether the proposed OSSF location is within a floodplain. Compliance with floodplain regulations is mandatory. 3. Fees: 4. Review and Approval Process: Plan Review: Upon submission, the Inspections Department will review your application and supporting materials to ensure compliance with all regulations. Inspections: After installation, but before covering any components, schedule an inspection with the department to verify that the system is installed according to the approved plans and standards. Approval: Once the system passes inspection, you'll receive authorization to operate the OSSF. 5. Additional Considerations: Licensed Contractors: All OSSF work must be completed by contractors licensed by the State of Texas and registered with the City of Mineral Wells. Regulatory Compliance: Always verify with the Inspections Department for any updates or changes to application requirements or regulations before proceeding. Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with the City's Inspections Department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. In Parker County, Texas, the Parker County Permitting Department serves as the Authorized Agent for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) concerning On-Site Sewage Facilities (OSSFs), commonly known as septic systems. As the Authorized Agent, the department is responsible for implementing and enforcing state regulations related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs within the county. Key Responsibilities of the Parker County Permitting Department as an Authorized Agent: Permitting and Plan Review: Inspections: Enforcement and Compliance: Public Education and Assistance: By fulfilling these responsibilities, the Parker County Permitting Department ensures that on-site sewage systems are designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that safeguards public health and preserves environmental quality. Contact Information: For detailed information on application procedures, required documentation, and other OSSF-related inquiries, it is advisable to contact the department directly or visit their official website. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. Managing a septic system within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires compliance with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here are the key considerations: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Reno has established ordinances governing the installation and maintenance of septic systems to prevent health hazards and environmental pollution. These ordinances may include requirements such as obtaining permits for all OSSF-related work, regardless of property size, and mandating that maintenance be performed by licensed professionals or homeowners who have completed approved maintenance courses. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than installing or maintaining a private septic system. For instance, the City of Parker mandates connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field In Parker County, Texas, maintaining compliance for your on-site sewage facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, involves adhering to specific renewal and reporting requirements. These requirements can vary based on the type of system you have and your specific location within the county. 1. Maintenance Contracts: Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs): These systems typically require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. The Texas Health and Safety Code mandates that aerobic systems be covered by a continuous service policy for the first two years after installation. After this initial period, homeowners must either renew the maintenance contract or, if qualified, maintain the system themselves. Self-maintenance is permissible only if the homeowner has completed a TCEQ-approved course on aerobic system maintenance. Renewal Frequency: Maintenance contracts are typically renewed annually. It's essential to ensure that your system is always under a valid contract to comply with state and local regulations. 2. Reporting Requirements: Routine Inspections: For systems under a maintenance contract, the service provider is required to perform inspections and submit reports to the local permitting authority. The frequency of these inspections and reports is generally every four months, resulting in three reports per year. However, if your system is equipped with advanced electronic monitoring, the reporting frequency may be reduced to every six months. Self-Maintained Systems: If you're maintaining the system yourself, you must adhere to the same inspection and reporting schedule. Reports should detail the system's operational status, any maintenance performed, and any issues identified. These reports must be submitted to the Parker County Permitting Department within 14 days of the inspection. 3. Local Ordinances: Recommendations: Stay Informed: Regularly consult with the Parker County Permitting Department and your local city authorities to stay updated on any changes in regulations or requirements. Maintain Records: Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities, contracts, and reports. This documentation is crucial for compliance and can be beneficial if any issues arise. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any service providers you hire are licensed and familiar with both state and local regulations pertaining to septic systems. By adhering to these guidelines and maintaining open communication with local authorities, you can ensure your septic system remains compliant and functions efficiently. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ Managing an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires adherence to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate OSSFs within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Parker mandates that septic system plans, drawings, and final inspection reports be filed with the city prior to the house's final approval. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than maintaining a private septic system. The City of Parker, for instance, requires connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. When planning to install or modify an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Aledo, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Application Submission: Obtain Application Forms: The City of Aledo requires that all OSSFs be permitted as part of the building permit process for new construction, repairs, or remodeling projects. You can access the necessary application forms through the city's official website. Site Evaluation: A licensed Site Evaluator or Professional Engineer must conduct a site and soil evaluation to determine the suitability of your property for an OSSF. This evaluation is crucial for designing an effective system. System Design: Based on the site evaluation, develop a system design that complies with state and local regulations. The design should include detailed plans and specifications of the proposed OSSF. 2. Supporting Materials: Property Plat or Survey: Provide a detailed plat or survey of your property, clearly indicating boundaries, existing structures, proposed OSSF location, and distances from property lines and water sources. Soil Analysis Report: Include the results of the soil analysis conducted during the site evaluation, highlighting soil types and their suitability for wastewater absorption. Floodplain Information: If applicable, provide documentation indicating whether the proposed OSSF location is within a floodplain. Compliance with floodplain regulations is mandatory. 3. Fees: 4. Review and Approval Process: Plan Review: Upon submission, the Permits Department will review your application and supporting materials to ensure compliance with all regulations. Inspections: After installation, but before covering any components, schedule an inspection with the department to verify that the system is installed according to the approved plans and standards. Approval: Once the system passes inspection, you'll receive authorization to operate the OSSF. 5. Additional Considerations: Connection to Public Sewer: The City of Aledo mandates that no permit shall be issued for an OSSF if a public sanitary sewer is available. Ensure that your property does not have access to a public sewer system before applying for an OSSF permit. Maintenance Contracts: Certain systems, especially aerobic treatment units, may require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. Ensure you understand and comply with any ongoing maintenance requirements. Regulatory Compliance: Always verify with the Permits Department for any updates or changes to application requirements or regulations before proceeding. Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with the City's Permits Department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. In Parker County, Texas, the Parker County Permitting Department serves as the Authorized Agent for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) concerning On-Site Sewage Facilities (OSSFs), commonly known as septic systems. As the Authorized Agent, the department is responsible for implementing and enforcing state regulations related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs within the county. Key Responsibilities of the Parker County Permitting Department as an Authorized Agent: Permitting and Plan Review: Inspections: Enforcement and Compliance: Public Education and Assistance: By fulfilling these responsibilities, the Parker County Permitting Department ensures that on-site sewage systems are designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that safeguards public health and preserves environmental quality. Contact Information: For detailed information on application procedures, required documentation, and other OSSF-related inquiries, it is advisable to contact the department directly or visit their official website. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. Managing a septic system within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires compliance with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here are the key considerations: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Reno has established ordinances governing the installation and maintenance of septic systems to prevent health hazards and environmental pollution. These ordinances may include requirements such as obtaining permits for all OSSF-related work, regardless of property size, and mandating that maintenance be performed by licensed professionals or homeowners who have completed approved maintenance courses. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than installing or maintaining a private septic system. For instance, the City of Parker mandates connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field In Parker County, Texas, maintaining compliance for your on-site sewage facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, involves adhering to specific renewal and reporting requirements. These requirements can vary based on the type of system you have and your specific location within the county. 1. Maintenance Contracts: Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs): These systems typically require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. The Texas Health and Safety Code mandates that aerobic systems be covered by a continuous service policy for the first two years after installation. After this initial period, homeowners must either renew the maintenance contract or, if qualified, maintain the system themselves. Self-maintenance is permissible only if the homeowner has completed a TCEQ-approved course on aerobic system maintenance. Renewal Frequency: Maintenance contracts are typically renewed annually. It's essential to ensure that your system is always under a valid contract to comply with state and local regulations. 2. Reporting Requirements: Routine Inspections: For systems under a maintenance contract, the service provider is required to perform inspections and submit reports to the local permitting authority. The frequency of these inspections and reports is generally every four months, resulting in three reports per year. However, if your system is equipped with advanced electronic monitoring, the reporting frequency may be reduced to every six months. Self-Maintained Systems: If you're maintaining the system yourself, you must adhere to the same inspection and reporting schedule. Reports should detail the system's operational status, any maintenance performed, and any issues identified. These reports must be submitted to the Parker County Permitting Department within 14 days of the inspection. 3. Local Ordinances: Recommendations: Stay Informed: Regularly consult with the Parker County Permitting Department and your local city authorities to stay updated on any changes in regulations or requirements. Maintain Records: Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities, contracts, and reports. This documentation is crucial for compliance and can be beneficial if any issues arise. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any service providers you hire are licensed and familiar with both state and local regulations pertaining to septic systems. By adhering to these guidelines and maintaining open communication with local authorities, you can ensure your septic system remains compliant and functions efficiently. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ Managing an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires adherence to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate OSSFs within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Parker mandates that septic system plans, drawings, and final inspection reports be filed with the city prior to the house's final approval. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than maintaining a private septic system. The City of Parker, for instance, requires connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. with state and local regulations. The design should include detailed plans and specifications of the proposed OSSF. 2. Supporting Materials: Property Plat or Survey: Provide a detailed plat or survey of your property, clearly indicating boundaries, existing structures, proposed OSSF location, and distances from property lines and water sources. Soil Analysis Report: Include the results of the soil analysis conducted during the site evaluation, highlighting soil types and their suitability for wastewater absorption. Floodplain Information: If applicable, provide documentation indicating whether the proposed OSSF location is within a floodplain. Compliance with floodplain regulations is mandatory. 3. Fees: 4. Review and Approval Process: Plan Review: Upon submission, the Building Division will review your application and supporting materials to ensure compliance with all regulations. Inspections: After installation, but before covering any components, schedule an inspection with the department to verify that the system is installed according to the approved plans and standards. Approval: Once the system passes inspection, you'll receive authorization to operate the OSSF. 5. Additional Considerations: Connection to Public Sewer: The City of Weatherford mandates that no permit shall be issued for an OSSF if a public sanitary sewer is available. Ensure that your property does not have access to a public sewer system before applying for an OSSF permit. Maintenance Contracts: Certain systems, especially aerobic treatment units, may require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. Ensure you understand and comply with any ongoing maintenance requirements. Regulatory Compliance: Always verify with the Building Division for any updates or changes to application requirements or regulations before proceeding. Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with the City's Building Division, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. In Parker County, Texas, the Parker County Permitting Department serves as the Authorized Agent for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) concerning On-Site Sewage Facilities (OSSFs), commonly known as septic systems. As the Authorized Agent, the department is responsible for implementing and enforcing state regulations related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs within the county. Key Responsibilities of the Parker County Permitting Department as an Authorized Agent: Permitting and Plan Review: Inspections: Enforcement and Compliance: Public Education and Assistance: By fulfilling these responsibilities, the Parker County Permitting Department ensures that on-site sewage systems are designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that safeguards public health and preserves environmental quality. Contact Information: For detailed information on application procedures, required documentation, and other OSSF-related inquiries, it is advisable to contact the department directly or visit their official website. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. Managing a septic system within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires compliance with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here are the key considerations: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Reno has established ordinances governing the installation and maintenance of septic systems to prevent health hazards and environmental pollution. These ordinances may include requirements such as obtaining permits for all OSSF-related work, regardless of property size, and mandating that maintenance be performed by licensed professionals or homeowners who have completed approved maintenance courses. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than installing or maintaining a private septic system. For instance, the City of Parker mandates connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ Managing a septic system in unincorporated areas of Parker County, Texas, requires adherence to specific regulations to ensure environmental safety and system efficiency. Here are the key considerations: 1. Permitting Requirements: 2. Local Regulations in Parker County: The Parker County Permitting Department oversees OSSFs in unincorporated areas. They regulate and issue permits for septic systems to ensure compliance with health and safety standards. 3. System Design and Maintenance: 4. Emergency Repairs: While emergency repairs (e.g., replacing tank lids, inlet and outlet devices) do not require a permit, they must be reported to the permitting authority in writing within 72 hours after repairs have begun. 5. Compliance and Inspections: For detailed information and assistance, contact the Parker County Permitting Department: Ensuring compliance with these regulations will help maintain the functionality of your septic system and protect the local environment. You can read more about compliance at this link: TCEQ Maintaining an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, in unincorporated areas of Parker County, Texas, requires adherence to specific operational and maintenance protocols to ensure environmental safety and system efficiency. Below are the key requirements and recommendations: 1. Routine Maintenance: 2. Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs): Maintenance Contracts: ATUs, which provide advanced treatment of wastewater, require more frequent maintenance. Texas regulations mandate that these systems be covered by a continuous service policy for the first two years after installation. After this period, homeowners must either renew the maintenance contract or, if qualified, maintain the system themselves. Self-Maintenance Eligibility: To personally maintain an ATU, homeowners must complete a Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ)-approved course on aerobic system maintenance. This ensures they have the necessary knowledge to manage the system effectively. 3. Reporting and Inspections: Routine Inspections: For systems under a maintenance contract, the service provider is required to perform inspections and submit reports to the local permitting authority. The frequency of these inspections is typically every four months, resulting in three reports per year. Self-Maintained Systems: Homeowners who have opted to maintain their own systems must adhere to the same inspection schedule and are responsible for submitting reports to the Parker County Permitting Department within 14 days of each inspection. 4. Regulatory Compliance: Permitting: Any construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF requires a permit from the Parker County Permitting Department. Unauthorized work can lead to penalties and potential system failures. Licensed Professionals: All maintenance and repair work should be conducted by professionals licensed by the TCEQ, ensuring that all tasks meet state and local standards. 5. Additional Recommendations: Water Conservation: Implementing water-saving measures reduces the load on your septic system, prolonging its lifespan and efficiency. Proper Waste Disposal: Avoid disposing of non-biodegradable items, grease, or hazardous chemicals down the drain, as they can disrupt the system's operation and lead to contamination. Regular Inspections: Even with routine maintenance, periodic professional inspections can help identify potential issues before they become major problems. By adhering to these guidelines and maintaining open communication with the Parker County Permitting Department, you can ensure the longevity and proper functioning of your septic system, safeguarding both your property and the environment. An aerobic septic system in Parker or Johnson County, Texas, is an on-site sewage facility (OSSF) designed to treat and dispose of wastewater using aerobic (oxygen-loving) bacteria. These systems are often used in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible due to soil conditions, space limitations, or environmental concerns. To install or modify an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) in unincorporated areas of Parker County, Texas, you must adhere to specific application requirements set forth by the Parker County Permitting Department and the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Application Submission: 2. Supporting Materials: 3. Fees: 4. Review and Approval Process: 5. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with the Parker County Permitting Department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. When installing or modifying an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF) within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, it's essential to adhere to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Determine the Local Permitting Authority: 2. Application Submission: 3. Supporting Materials: 4. Fees: 5. Review and Approval Process: 6. Additional Considerations: Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and collaborating closely with your city's permitting department, you can ensure a smooth application process and the successful installation or modification of your septic system. There are 4 treatment component steps of an Aerobic Septic System. The Pretreatment Tank is the initial tank where solids settle, similar to a conventional septic tank. The next treatment step is where air is introduced to the wastewater to promote aerobic bacterial activity. The third step is the disinfection step. This is where treated water is disinfected using chlorine, ltraviolet light or other methods. The final step is where the treated water is either dispersed throughout a surface (spray irrigation ) or a subsurface drain field In Parker County, Texas, maintaining compliance for your on-site sewage facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, involves adhering to specific renewal and reporting requirements. These requirements can vary based on the type of system you have and your specific location within the county. 1. Maintenance Contracts: Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs): These systems typically require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. The Texas Health and Safety Code mandates that aerobic systems be covered by a continuous service policy for the first two years after installation. After this initial period, homeowners must either renew the maintenance contract or, if qualified, maintain the system themselves. Self-maintenance is permissible only if the homeowner has completed a TCEQ-approved course on aerobic system maintenance. Renewal Frequency: Maintenance contracts are typically renewed annually. It's essential to ensure that your system is always under a valid contract to comply with state and local regulations. 2. Reporting Requirements: Routine Inspections: For systems under a maintenance contract, the service provider is required to perform inspections and submit reports to the local permitting authority. The frequency of these inspections and reports is generally every four months, resulting in three reports per year. However, if your system is equipped with advanced electronic monitoring, the reporting frequency may be reduced to every six months. Self-Maintained Systems: If you're maintaining the system yourself, you must adhere to the same inspection and reporting schedule. Reports should detail the system's operational status, any maintenance performed, and any issues identified. These reports must be submitted to the Parker County Permitting Department within 14 days of the inspection. 3. Local Ordinances: Recommendations: Stay Informed: Regularly consult with the Parker County Permitting Department and your local city authorities to stay updated on any changes in regulations or requirements. Maintain Records: Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities, contracts, and reports. This documentation is crucial for compliance and can be beneficial if any issues arise. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any service providers you hire are licensed and familiar with both state and local regulations pertaining to septic systems. By adhering to these guidelines and maintaining open communication with local authorities, you can ensure your septic system remains compliant and functions efficiently. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ Managing an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires adherence to both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate OSSFs within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Parker mandates that septic system plans, drawings, and final inspection reports be filed with the city prior to the house's final approval. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than maintaining a private septic system. The City of Parker, for instance, requires connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. The system introduces air into the wastewater treatment process to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down organic matter more effectively than anaerobic bacteria used in conventional systems The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) serves as an authorized agent in Texas, primarily overseeing the regulation of on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. This authorization empowers TRWD to implement and enforce rules concerning the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs, ensuring they meet or exceed the standards set by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). By adopting and enforcing these regulations, TRWD aims to prevent pollution and protect public health within its service areas. In its capacity as an authorized agent, TRWD's responsibilities include: Permitting and Inspection: Issuing permits for the installation and modification of OSSFs and conducting inspections to ensure compliance with established standards. Enforcement: Taking necessary actions to address violations, which may involve fines or other corrective measures to ensure adherence to OSSF regulations. Public Education: Providing information and resources to the community about proper OSSF practices to promote environmental stewardship and public health. Additionally, TRWD's Law Enforcement Division (LED) plays a crucial role in environmental enforcement. Their duties encompass investigating environmental violations such as hazardous material spills, septic violations, and illegal dumping. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of water resources and the surrounding environment. Through these combined efforts, TRWD ensures the effective management of water resources and the protection of public health and the environment within its jurisdiction. In Parker County, Texas, the Parker County Permitting Department serves as the Authorized Agent for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) concerning On-Site Sewage Facilities (OSSFs), commonly known as septic systems. As the Authorized Agent, the department is responsible for implementing and enforcing state regulations related to the installation, operation, and maintenance of OSSFs within the county. Key Responsibilities of the Parker County Permitting Department as an Authorized Agent: Permitting and Plan Review: Inspections: Enforcement and Compliance: Public Education and Assistance: By fulfilling these responsibilities, the Parker County Permitting Department ensures that on-site sewage systems are designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that safeguards public health and preserves environmental quality. Contact Information: For detailed information on application procedures, required documentation, and other OSSF-related inquiries, it is advisable to contact the department directly or visit their official website. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) does not oversee all counties in Texas. Instead, it primarily serves Tarrant County and parts of North Texas, managing water resources, flood control, and water conservation. No, TRWD does not regulate septic systems (OSSFs) in all Texas counties. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) delegates OSSF regulation to county environmental health departments or regional authorized agents within each county. For example: TRWD is a regional water authority focusing on water supply, flood control, and watershed protection in Tarrant County and surrounding North Texas areas. However, it does not oversee all counties in Texas—each county typically manages its own OSSF (septic) permitting and water regulations through county or municipal agencies. The Tarrant Regional Water District (TRWD) is a significant water resource entity in North Texas, overseeing various projects across multiple counties to ensure reliable water supply, effective flood control, and recreational opportunities. Here's an overview of TRWD's key projects and initiatives by county: 1. Tarrant County: Water Supply and Flood Control: TRWD manages reservoirs and infrastructure to provide water to over 2 million residents and implements flood control measures within Tarrant County. Recreational Facilities: The district maintains and develops recreational areas such as the Trinity Trails, Airfield Falls, Twin Points Park, and Eagle Mountain Park, offering residents various outdoor activities. 2. Dallas County: 3. Henderson and Navarro Counties: Cedar Creek and Richland-Chambers Reservoirs: Located in Henderson and Navarro counties, respectively, these reservoirs are crucial components of TRWD's water supply system, providing significant water resources to the region. George W. Shannon Wetlands: Adjacent to the Richland-Chambers Reservoir in Navarro County, this 2,000-acre wetland project naturally filters water from the Trinity River, enhancing water quality and supply. 4. Anderson County: 5. Wise and Jack Counties: 6. Parker County: Through these projects and collaborations, TRWD plays a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding water resources across multiple North Texas counties, ensuring sustainable water supply, flood protection, and recreational amenities for the region's growing population. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is a governmental agency responsible for managing the water resources of the Brazos River basin, which spans 42,000 square miles across Texas. The Brazos River is the longest river entirely within Texas, flowing 840 miles from its headwaters in the Texas Panhandle to the Gulf of Mexico. The BRA was created in 1929 as the first river authority in the United States to develop, manage, and protect water resources within a single river basin. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) plays a vital role in water supply management, flood control, water quality, and conservation within the Brazos River Basin. It ensures reliable water resources for cities, businesses, agriculture, and recreation while protecting water quality and ecosystems. Setbacks: Systems must meet distance requirements from property lines, water wells, and surface water. See city specifc questions for more detail. The Brazos River Authority (BRA) is instrumental in managing water resources across the Brazos River basin in Texas. Beyond its primary responsibilities, the BRA oversees several reservoirs and is engaged in numerous projects to enhance water supply, quality, and infrastructure. Key Reservoirs Managed by the BRA: Possum Kingdom Lake: Lake Granbury: Lake Limestone: Allens Creek Reservoir (Proposed): Notable Projects and Initiatives: East Williamson County Regional Water System (EWCRWS) Expansion: Morris Sheppard Dam – Possum Kingdom Lake: Environmental and Special Projects: Through the management of these reservoirs and the execution of various projects, the BRA continues to play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable water resources, environmental stewardship, and infrastructure development within the Brazos River basin. Managing a septic system within the city limits of Parker County, Texas, requires compliance with both state regulations and specific municipal ordinances. Here are the key considerations: 1. Municipal Regulations: City Authority: Each city within Parker County has the authority to regulate on-site sewage facilities (OSSFs) within its jurisdiction. For example, the City of Reno has established ordinances governing the installation and maintenance of septic systems to prevent health hazards and environmental pollution. These ordinances may include requirements such as obtaining permits for all OSSF-related work, regardless of property size, and mandating that maintenance be performed by licensed professionals or homeowners who have completed approved maintenance courses. Connection to Municipal Sewer: If a municipal sanitary sewer system is accessible, property owners are typically required to connect to it rather than installing or maintaining a private septic system. For instance, the City of Parker mandates connection to the municipal sewer if a sanitary sewer line is available to the site, at the landowner's cost. 2. State Regulations: Permitting: The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) requires a permit for the construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF. While local authorities often handle permitting, it's essential to ensure that all state requirements are met. Design and Maintenance: OSSFs must be designed based on a site evaluation that considers local conditions. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the system functions correctly and complies with health standards. Recommendations: Consult Local Authorities: Contact your city's permitting or public works department to obtain specific regulations, permit requirements, and guidelines related to septic systems. Each city may have unique ordinances that affect OSSF installation and maintenance. Engage Licensed Professionals: Ensure that any work on your septic system is performed by licensed installers or maintenance providers, as required by state and local regulations. Stay Informed: Regularly review both state and local regulations to remain compliant, as rules and ordinances can change over time. By adhering to both state and municipal regulations, you can ensure the proper functioning of your septic system and contribute to public health and environmental protection. You can find more information at this link: TCEQ In unincorporated areas of Parker County, Texas, the installation, modification, or repair of an On-Site Sewage Facility (OSSF), commonly known as a septic system, requires adherence to specific approval and inspection procedures. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you: 1. Application and Approval Process: Permit Requirement: Before commencing any construction, installation, alteration, extension, or repair of an OSSF, you must obtain a permit from the Parker County Permitting Department. Unauthorized construction can lead to civil and administrative penalties. Application Submission: Complete the "On-Site Sewage Facility Application," providing detailed information about your property and the proposed system. This includes a site evaluation conducted by a licensed Site Evaluator or Professional Engineer to assess soil suitability and site-specific conditions. System Design: Based on the site evaluation, develop a system design that complies with state and local regulations. The design should include detailed plans and specifications of the proposed OSSF. 2. Inspection Process: Construction Inspection: After obtaining the permit and during the installation of the OSSF, but before covering any components, you must schedule an inspection with the Parker County Permitting Department. This inspection ensures the system is installed according to the approved plans and complies with regulatory standards. Final Approval: Once the system passes the inspection, you'll receive authorization to operate the OSSF. It's crucial to ensure that all components are accessible and that the system is functioning correctly before the final approval. 3. Additional Considerations: Maintenance Requirements: Certain systems, especially aerobic treatment units, may require a maintenance contract with a licensed service provider. Ensure you understand and comply with any ongoing maintenance requirements to keep the system functioning properly and in compliance with regulations. Regulatory Compliance: Always verify with the Parker County Permitting Department for any updates or changes to application requirements or regulations before proceeding. Staying informed ensures compliance and helps avoid potential issues. Contact Information: By meticulously following these steps and maintaining open communication with the Parker County Permitting Department, you can ensure a smooth approval and inspection process for your septic system in unincorporated areas of Parker County. You can find the Parker County Permitting Application here: https://www.parkercountytx.gov/DocumentCenter/View/10724/Parker-County-Septic-Application-and-Tech-Sheet State & Local Requirements
How Does Your Region Affect Septic Installation?
Considerations For Parker County
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For City of Willow
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For City of Hudson Oaks
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For Wise County
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For Erath County
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For Palo Pinto County
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For Granbury
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For Hood County
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For City of Joshua
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For Johnson County
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For City of Cleburne
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For City of Reno
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For City of Fort Worth
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For City of Mineral Wells
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For City of Aledo
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For City of Weatherford
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.Considerations For Parker County
Jurisdiction and Responsibilities of TRWD:
Does TRWD Regulate On-Site Sewage (OSSFs) in Other Counties?
Conclusion:
Key Responsibilities of the Brazos River Authority:
1. Water Supply Management
2. Flood Control and Drought Management
3. Water Quality Protection
4. Permitting and Water Rights
5. Recreational and Environmental Stewardship
Service Area of the Brazos River Authority
Governance of the Brazos River Authority
Conclusion
Floodplains: Additional regulations may apply if the property is in a floodplain.
Variances: May be required for non-standard installations or properties with unique conditions. Routine pumping and maintenance are the homeowner's responsibility. Keep records of pumping and any repairs. Aerobic Systems must have a continuous maintenance contract with a licensed provide. Maintenance providers are required to submit inspection reports to the permitting authority.

MAINTENANCE PLAN
Maintain Your System With A HomeField Advantage Plan
Owning a septic system in Parker County means following local regulations. We’ve built our HomeField Advantage Plans to make caring for your septic system simple.

ONE CALL FOR ALL
Tired of calling around? One call to HomeField Parker County gets a team member right at your door, ready to take care of all your septic system needs.

A Proactive Home team
Want to avoid future problems? Our home team of septic experts work proactively for you, and our predictable pricing is so that you have no surprises along the way.

WIN NOW AND LATER
Want to win? Our Advantage Plans are designed to give you peace of mind around your septic system. We’re here to help you and your system as long as you need us.
Looking For A Commercial Plan?
TESTIMONIALS
What Our Customers Are Saying About Us
We’re here to give our customers around Parker County peace of mind whenever they think about their septic system. Here’s what they’ve been saying about our service.
Super friendly, super professional! This will be the only company that I ever use again. They are honest, hard working and very knowledgeable. #1 in my book.
Had a septic issue and they were the only company able to make it out the next day. Highly recommend this company. Really friendly and knowledgeable.
Love the service of this company! Very professional and the people are so knowledgeable and nice. Would recommend their services to anyone.
They came out to our property to diagnose why the alarm was going off. They fixed the problem and educated me on best practices. I highly recommend their services because of their friendly professionalism and expertise!
I’ve been extremely satisfied with their service. I’m a monthly service plan member and recently had an issue with my aerobic system on a Friday afternoon. I called and was impressed with the speed of getting a technician onsite to repair my system. They communicated via SMS in a very timely manner and resolved my issue very quickly. Highly recommend!!
Love love love this company!! They always have done a great job!! Very knowledgeable! They always get the job done! They are reliable and very honest! I could not recommend them more!! Great company! Thank you!
We have a service contract, and everyone we deal with has always been so helpful. They are quick to respond, and help us learn about our system.
I am a professional builder and Brian is the best. He is fair in his pricing and he does an excellent job from design to installation. You can rely on Brian for a trouble free construction experience.
Excellent service, in a timely & professional manner, at a fair price. They have excellent service for our aerobic system with a yearly contract at a fair price. Definitely recommend to anyone. A company you can count on consistently!
Showed up on time…in the middle of a severe storm and performed the work anyway. The young man had a positive attitude and the rain didn’t seem to phase him. Nasty conditions but performed like it was a beautiful sunny day. He took photos like I asked and documented the process. Thank you for your professionalism
Wonderful customer service, came out and fix the problem on the septic system and gave me a quick training on how to maintain good working order. Thank you for your excellent customer service!
These guys are real professional. They know their stuff. They even suggest ways that you can make your septic tank last longer and work more efficient. I will recommend them as the best septic tank company that I have ever used!!
I had an issue with my aerobic system at my home in Cedar Hill and called them at 8am. They came and had my issue fixed shortly around noon. I signed up for their annual maintenance service at a very reasonable price.
I called on the 16th of January in the midst of a hard freeze due to my septic system alarm going off. Even with the weather and its associated workload, the techs arrived the same day and resolved the issue. Awesome service seems to be the norm for this company and their techs!
Great service. We received service within a few hours of calling in. They came in and found the issue immediately and provided great tips and feedback. We know nothing about the septic tank so the info gathered was very helpful.
OUR PROCESS
The Game Plan For Your Septic System Installation
Whatever commercial system you’re installing, you need to get your new system into the ground, hooked up, and ready for operation. We make that happen for you.

We’ll Assess The Area First
We’ll evaluate your site and soil to see if they’re suitable for your system, then get the permits and approvals we need to start.

We Dig Your Tank’s Home
We’ll dig the perfect size home for your septic tank along with any trenches your system might need to connect to the rest of its parts.

Position And Connect
OK, this part IS technical, but in short we’ll put your septic tank in place then securely connect the parts that make up your septic system.

Installing Your Home Field
Next we’ll install the right type of dispersal field for your specific septic system, giving your treated wastewater somewhere to go.

We’ll Make Sure It Works
We’ll inspect your completed septic system, make sure it works, ensure it meets all of your regional codes, and then tidy up around your property.
Get Your New System Installed...



OUR SERVICE AREA
WE LOVE OURHOME TURF
We proudly serve our home turf of Parker, Johnson, and Hood county, including the following cities and towns:
